Improving Survival Rates for Mouth Cancer: Advances in Detection and Treatment
Mouth cancer, commonly known as oral cancer, is a major health concern worldwide. While the frequency varies by region, the impact on impacted individuals and healthcare systems is severe. Fortunately, advances in diagnostic and treatment procedures have contributed to higher mouth cancer survival rate in patients. If we talk about mouth cancer survival rate by age, people aged 45 to 54 have an average 5-year survival rate of 89.4%, whereas those aged 55 to 64 have a 75.6% 5-year survival rate. Those who are 65 and above have a 61.9% 5-year survival rate when we analyze mouth cancer survival rate by age. In this article, we discuss the subtleties of mouth cancer and the factors important in improving mouth cancer treatment success rate.
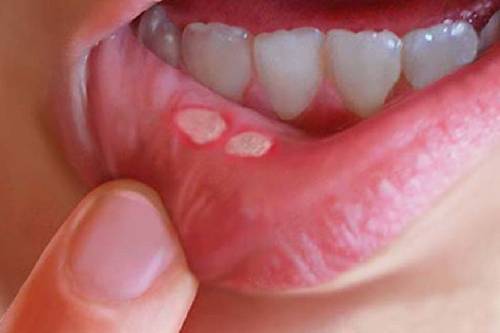
Understanding Mouth Cancer
Mouth cancer refers to malignancies that develop in the oral cavity, which includes the lips, tongue, gums, palate, and inner cheek lining. It frequently appears as squamous cell carcinoma, a cancer that develops in the mouth's squamous cells. Tobacco usage, heavy alcohol use, human papillomavirus (HPV) infection, poor oral hygiene, and a low-fruit and vegetable diet all increase the risk of developing mouth cancer. Mouth cancer symptoms might include persistent ulcers, red or white patches in the mouth, trouble swallowing or chewing, a persistent sore throat, and swelling or lumps in the mouth or neck. Early identification of mouth cancer is crucial for timely treatment and a better prognosis for an improved mouth cancer treatment success rate.
How Have Survival Rates for Mouth Cancer Improved?
Over time, mouth cancer survival rate have improved significantly, owing to advances in early detection tools, treatment modalities, and supportive care measures. Increased understanding of mouth cancer risk factors and symptoms has resulted in earlier detection and care, which has contributed to improved mouth cancer survival rate.
Advances in Detection of Mouth Cancer
One of the primary factors driving increases in mouth cancer survival rate is the development of more sensitive and precise diagnosis techniques. Traditional screening procedures like visual inspection and palpation are still useful diagnostic tools, but technological advancements have broadened the scope of early detection.
Emerging technologies, including fluorescence imaging, brush biopsy, and optical coherence tomography (OCT), allow clinicians to discover precancerous and cancerous lesions at an early stage when treatment is most effective. These non-invasive and minimally invasive procedures allow for more precise detection of concerning lesions, lowering the risk of missed diagnoses and delayed treatment.
Fluorescence Imaging
Fluorescence imaging uses fluorescent dyes or light-emitting probes to highlight aberrant tissues in the mouth cavity. Fluorescence imaging enhances the contrast between healthy and sick tissues, allowing the visibility of tiny alterations that may reveal the presence of malignant or precancerous tumors.
Brush biopsy
Brush biopsy, also known as exfoliative cytology, is the process of gently brushing the surface of suspected tumors to collect cells for examination under a microscope. This minimally invasive process allows clinicians to collect cellular samples from places that are difficult to reach with typical biopsy methods, allowing for early diagnosis and intervention.
Optical Coherence Tomography
Optical coherence tomography (OCT) is a non-invasive imaging method that produces high-resolution cross-sectional images of tissue features in the mouth cavity. OCT, which captures comprehensive images of tissue morphology and architecture, enables the early detection of aberrant changes associated with mouth cancer. It helps guide doctors through the diagnosis and treatment planning process to improve mouth cancer treatment success rate.
Advances in the Treatment of Mouth Cancer
Treatment options to improve mouth cancer survival rate have also developed significantly, allowing patients to get more tailored and effective therapeutic approaches. The treatment technique is determined by the cancer's stage and location, as well as the patient's overall health status and treatment preferences.
Surgery
Surgery is still the primary treatment for mouth cancer, especially in the early stages. Surgical techniques have improved, enabling accurate tumor removal while preserving important tissues and functions in the mouth and face. Furthermore, reconstructive surgery techniques allow doctors to regain aesthetics and function after substantial tumor removal.
Radiation Therapy
Radiation therapy, targeted therapy, chemotherapy, and immunotherapy are some of the different treatment options for mouth cancer besides surgery. Radiation therapy advancements, such as intensity-modulated radiation therapy (IMRT) and proton therapy, deliver higher doses of radiation to cancer cells while limiting damage to healthy tissues.
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy can be used alone or in tandem with other treatment options to increase mouth cancer survival rate. Chemotherapeutic drugs target cancer cells that divide rapidly, preventing them from growing and spreading. By adding chemotherapy to multimodal treatment regimens, healthcare practitioners can improve treatment efficacy and patient outcomes.
Targeted Therapy and Immunotherapy
Targeted therapy and immunotherapy medications, which use specific molecular pathways or the body's immune system to fight cancer, have shown positive results in some cases of advanced or recurring mouth cancer. These targeted techniques present new opportunities for individualized treatment and a better mouth cancer survival rate for patients with specific genetic mutations or immunological profiles.
Conclusion
Advancements in chemotherapy have led to increased mouth cancer survival rate and treatment results for people with mouth cancer. The field of study for mouth cancer care is evolving, with breakthrough techniques for diagnosis and customized therapy methods providing hope and optimism for both patients and healthcare providers. There are several clinics with high mouth cancer treatment success rate using innovative techniques for diagnosis and treatment. One such clinic is Oncare Cancer. We offer an extensive diagnostic and treatment plan for a better mouth cancer survival rate.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
The survival rate for mouth cancer varies depending on several factors, including the stage of the cancer, the treatment received, and the particular patient's features. On average, the five-year survival rate for mouth cancer ranges between 60% and 70%. However, survival rates might vary significantly among patients depending on factors such as early detection, treatment adherence, overall health state, and cancer aggressiveness. Timely diagnosis and appropriate treatment options are critical for improving survival rates.
Several factors influence the survival rates of mouth cancer. These include the stage of cancer upon diagnosis, tumor size, position within the oral cavity, histological grade (degree of cell abnormalities), metastasis (spread to distant organs), the patient's overall health status, and treatment response. Early detection, access to quality healthcare, effective treatment options, and willingness to commit to treatment programs are critical factors that can improve survival results.
The stage of mouth cancer has a major effect on mouth cancer survival rate. Early-stage mouth cancers, defined as those in which the tumor is confined and has not progressed beyond the initial site, have a greater survival rate. Advanced-stage mouth cancers, which are distinguished by serious local invasion or distant tumors, have worse survival rates due to the difficulties involved with treatment and disease progression. Early detection and treatments are crucial in increasing survival rates for mouth cancer patients.
Several treatments can help people who have mouth cancer survive longer. These treatments include surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, targeted therapy, and immunotherapy. The stage of cancer, tumor features, the patient's overall health, and therapy goals all influence the treatment decision. Multimodal treatment techniques, which mix various medicines customized to specific patient needs, have been demonstrated to increase treatment efficacy and enhance long-term survival rates. Furthermore, innovations in treatment approaches and supportive care measures help to improve survival rates and quality of life for mouth cancer patients.